How To Get Rid Of Fungal Acne On Forehead
Noticing more facial blemishes than usual? Or little bumps on your face and body that just won't go away? You might have fallen prey to a particular type of skin condition – fungal acne . While this may sound intimidating, it is both normal and treatable.

What is fungal acne?
Fungal acne ( pityrosporum (malassezia) folliculitis ) appears very similarly to regular acne ( acne vulgaris ). While often mistaken for regular acne, the cause is different.
Sebaceous , or oil glands, naturally keep our skin moist and act as a first line of defense against bacteria. Fungal acne occurs as a response to an overgrowth of yeast that occurs within the hair follicles. When there is an imbalance of yeast in the sebaceous glands, your hair follicles may become inflamed thus, leading to fungal acne, which presents itself as .
What does fungal acne look like?
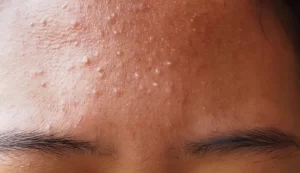
Fungal acne usually appears like a typical white head (minus the actual head) surrounded by redness of varying degrees. It commonly appears on oily areas such as the T-zone (forehead, nose, and chin), chest, and back. The bumps may be exacerbated by sweat or over-moisturizing. Additionally, being in a humid climate can increase your likelihood of developing fungal acne, as yeast thrive and grow in this type of environment.
Fungal Acne Vs. Regular Acne
Although regular acne and fungal acne have some similarities, there are several factors that can be used to distinguish one from the other.
How fungal acne feels vs regular acne
Fungal Acne: itching and burning
Regular Acne: neutral to varying degrees of pain
How fungal acne looks vs regular acne
Fungal Acne: white with red surrounding; bumps are uniform in size and usually occur in clusters
Regular Acne: varying appearances(i.e. white head or black head) and sizes with any combination of whiteheads, blackheads, skin-colored bumps or cysts; blemishes are more spaced out
Where fungal acne is located vs regular acne
Fungal Acne: oily areas such as the T-zone, chest, back, and arms
Regular Acne: anywhere on your face (forehead, nose, cheeks, chin, jawlin, hairline, temples), neck, chest, or back
What fungal acne is caused by vs regular acne
Fungal Acne: fungus (yeast)
Regular Acne: bacteria
How fungal acne is treated vs regular acne
Fungal Acne: change in diet (cut out/down sugar and carbs), bentonite clay masks, chemical exfoliants (lactic/salicylic acid), dandruff body wash, antifungal creams or medications, natural antifungals (oil of oregano, clove, walnut), increased frequency of showers, and looser clothes
Regular Acne: change in diet (avoid inflammation-promoting foods), treatment of hormonal imbalances, increased water intake, bentonite clay masks, salicylic acid, topical retinoids, and oral antibiotics.
What causes fungal acne on your face?
Fungal acne appears on your face as a result of yeast overgrowth , which may be due to hormone imbalance, diet changes, trapped moisture, suppressed immune system, tight clothes, and/or humid environments. While having some fungus and bacteria is important, an imbalance can lead to an overgrowth of yeast. This substance can then enter into sebaceous glands by the hair follicle and cause inflammation/itchiness (a.k.a fungal acne).
How is fungal acne diagnosed?
Before treating fungal acne, it's a good idea to consult a healthcare professional to ensure that you do not have another, similar skin condition. While they may be able to recognize it right away, they may want to conduct a fungal test to rule out anything else.
Although you may want to jump into treatment as soon as possible, consulting a provider (specifically a dermatologist if possible) is necessary, as misdiagnosing your acne could lead to ineffective treatment. For instance, if you start oral antibiotics to treat your typical acne, it could lead to or worsen fungal acne due to a disruption of normal bacteria.
How is fungal acne on the face treated?
Oral antifungal medication
Oral antifungal medication works by either directly killing or preventing the growth of fungal cells. Azoles are the most commonly used because they interfere with enzymes that help create the fungal cell membrane. This type of medication is taken by mouth for a period of time that is prescribed by your doctor.
Antifungal shampoo or body wash
Antifungal shampoo and body wash help slow down the growth of fungi that cause infection. Most of these products can be purchased over-the-counter, but some may require prescription from a doctor. They are applied to the affected area and rinsed off either immediately or after a few minutes. While these products can be very effective, they could lead to side effects such as skin irritation and/or discoloration, oiliness/dryness of the hair or scalp, abnormal hair texture.
Prescription topical creams
If over-the-counter products do not make a difference in your fungal acne, your doctor may recommend a stronger topical medication. A common prescription is Ketoconazole 2% , which is applied twice a day for two to three weeks to help reduce the yeast on the skin, leading to a significant reduction in fungal acne.
Diet adjustments
An antifungal diet involves reducing intake of foods that promote yeast growth (i.e. refined sugar and white flour) and/or contain yeast (i.e. vinegar, mushrooms, and beer). While it's not necessary to completely eliminate these food groups from your diet, finding a balance with other whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, grains, and lean meats could make a difference in your skin.
Oil-free moisturizer
Oil-free moisturizer is a great product, as it provides moisture to the skin without introducing more oil that could get trapped by hair follicles. These can be purchased over-the-counter and applied as part of your daily skin care routine.
What's the takeaway?
Fungal acne differs from other types of acne in that it is caused by an imbalance of yeast on the skin. While it may initially be mistaken for your typical blemish, it should ideally be looked at by a dermatologist, who can help determine an appropriate type of treatment.
Thankfully, fungal acne is treatable and will likely go away within a short period of time. Furthermore, you do not need to feel ashamed or embarrassed if you suddenly notice the dreaded small bumps – sometimes they are simply caused by living your life and the best thing you can do is consult a doctor.

Frequently Asked Questions about Fungal Acne
How do you know if it's fungal acne?
Fungal acne typically appears as a cluster of small, uniform bumps on your cheeks, back, or chest. These bumps are usually painless and do not have blackheads, whiteheads, or cysts. Additionally, traditional treatments likely won't work – if you find that nothing seems to make your blemishes go away, you could have fungal acne.
Can you pop fungal acne?
Fungal acne isn't filled with pus, so even if you tried to pop it, nothing would come out. With that said, popping acne in general is not recommended, as it can lead to irritation and scarring.
Is fungal acne itchy?
Fungal acne may cause minor itching or burning. However, it typically feels less intense compared to other types of acne. Regardless, keeping your hands away from your face is a best practice, as this prevents you from pushing the fungus or bacteria deeper into the skin and spreading the acne to different parts of your body.
Is glycerin bad for fungal acne?
Fungal acne has mixed responses to glycerin . In some cases, this treatment causes the fungus to multiply, but in others, it completely kills it. Furthermore, you should consult your doctor before trying this method.
How long does fungal acne last?
Fungal acne typically lasts until it is treated and may require different methods for complete removal. The treatment could take a few weeks to be effective.
Disclaimer: The above information is for general informational purposes only and is NOT a substitute for professional medical advice. Always seek the advice of your doctor/primary care provider before starting or changing treatment.
How To Get Rid Of Fungal Acne On Forehead
Source: https://www.pandiahealth.com/resources/how-to-treat-fungal-acne-on-face/
Posted by: belangerawor1940.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Get Rid Of Fungal Acne On Forehead"
Post a Comment